C Functions ❮ Edit Details
In c, we can divide a large program into the basic building blocks known as function. The function contains the set of programming statements enclosed by {}. A function can be called multiple times to provide reusability and modularity to the C program. In other words, we can say that the collection of functions creates a program. The function is also known as procedureor subroutinein other programming languages.
Advantage of functions in C
There are the following advantages of C functions.
- By using functions, we can avoid rewriting same logic/code again and again in a program.
- We can call C functions any number of times in a program and from any place in a program.
- We can track a large C program easily when it is divided into multiple functions.
- Reusability is the main achievement of C functions.
- However, Function calling is always a overhead in a C program.
Function Aspects
There are three aspects of a C function.
- Function declaration A function must be declared globally in a c program to tell the compiler about the function name, function parameters, and return type.
- Function call Function can be called from anywhere in the program. The parameter list must not differ in function calling and function declaration. We must pass the same number of functions as it is declared in the function declaration.
- Function definition It contains the actual statements which are to be executed. It is the most important aspect to which the control comes when the function is called. Here, we must notice that only one value can be returned from the function.
| SN | C function aspects | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Function declaration | return_type function_name (argument list); |
| 2 | Function call | function_name (argument_list) |
| 3 | Function definition | return_type function_name (argument list) {function body;} |
The syntax of creating function in c language is given below:
return_type
- function_name(data_type parameter...){
- //code to be executed
- }
Types of Functions
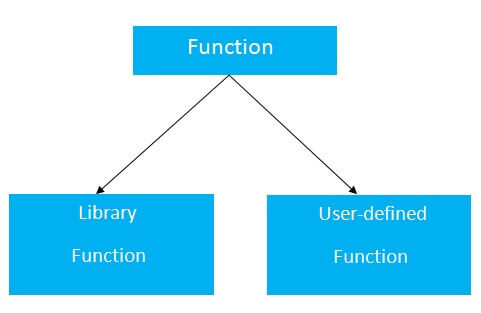
There are two types of functions in C programming:
- Library Functions: are the functions which are declared in the C header files such as scanf(), printf(), gets(), puts(), ceil(), floor() etc.
- User-defined functions: are the functions which are created by the C programmer, so that he/she can use it many times. It reduces the complexity of a big program and optimizes the code.
Return Value
A C function may or may not return a value from the function. If you don't have to return any value from the function, use void for the return type.
Let's see a simple example of C function that doesn't return any value from the function.
Example without return value:
- void hello(){
- printf("hello c");
- }
If you want to return any value from the function, you need to use any data type such as int, long, char, etc. The return type depends on the value to be returned from the function.
Let's see a simple example of C function that returns int value from the function.
Example with return value:
- int get(){
- return 10;
- }
In the above example, we have to return 10 as a value, so the return type is int. If you want to return floating-point value (e.g., 10.2, 3.1, 54.5, etc), you need to use float as the return type of the method.
- float get(){
- return 10.2;
- }
Now, you need to call the function, to get the value of the function.
Different aspects of function calling
A function may or may not accept any argument. It may or may not return any value. Based on these facts, There are four different aspects of function calls.
- function without arguments and without return value
- function without arguments and with return value
- function with arguments and without return value
- function with arguments and with return value
Example for Function without argument and return value
Example 1
- #include<stdio.h>
- void printName();
- void main ()
- {
- printf("Hello ");
- printName();
- }
- void printName()
- {
- printf("Javatpoint");
- }
-
Output
Hello Javatpoint
Example 2
- #include<stdio.h>
- void sum();
- void main()
- {
- printf("\nGoing to calculate the sum of two numbers:");
- sum();
- }
- void sum()
- {
- int a,b;
- printf("\nEnter two numbers");
- scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
- printf("The sum is %d",a+b);
- }
Output
Going to calculate the sum of two numbers: Enter two numbers 10 24 The sum is 34
Example for Function without argument and with return value
Example 1
- #include<stdio.h>
- int sum();
- void main()
- {
- int result;
- printf("\nGoing to calculate the sum of two numbers:");
- result = sum();
- printf("%d",result);
- }
- int sum()
- {
- int a,b;
- printf("\nEnter two numbers");
- scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
- return a+b;
- }
Output
Going to calculate the sum of two numbers: Enter two numbers 10 24 The sum is 34
Example 2: program to calculate the area of the square
- #include<stdio.h>
- int sum();
- void main()
- {
- printf("Going to calculate the area of the square\n");
- float area = square();
- printf("The area of the square: %f\n",area);
- }
- int square()
- {
- float side;
- printf("Enter the length of the side in meters: ");
- scanf("%f",&side);
- return side * side;
- }
Output
Going to calculate the area of the square Enter the length of the side in meters: 10 The area of the square: 100.000000
Example for Function with argument and without return value
Example 1
Output
Going to calculate the sum of two numbers: Enter two numbers 10 24 The sum is 34
Example 2: program to calculate the average of five numbers.
Output
Going to calculate the averag
- #include<stdio.h>
- void sum(int, int);
- void main()
- {
- int a,b,result;
- printf("\nGoing to calculate the sum of two numbers:");
- printf("\nEnter two numbers:");
- scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
- sum(a,b);
- }
- void sum(int a, int b)
- {
- printf("\nThe sum is %d",a+b);
- }
- #include<stdio.h>
- void average(int, int, int, int, int);
- void main()
- {
- int a,b,c,d,e;
- printf("\nGoing to calculate the average of five numbers:");
- printf("\nEnter five numbers:");
- scanf("%d %d %d %d %d",&a,&b,&c,&d,&e);
- average(a,b,c,d,e);
- }
- void average(int a, int b, int c, int d, int e)
- {
- float avg;
- avg = (a+b+c+d+e)/5;
- printf("The average of given five numbers : %f",avg);
- }
e of five numbers: Enter five numbers:10 20 30 40 50 The average of given five numbers : 30.000000
Example for Function with argument and with return value
Example 1
#include<stdio.h> int sum(int, int); void main()
Output
Going to calculate the sum of two numbers: Enter two numbers:10 20 The sum is : 30
Example 2: Program to check whether a number is even or odd
#include<stdio.h> int even_odd(int); void main() { int n,flag=0; printf("\nGoing to check whether a number is even or odd"); printf("\nEnter the number: ");
Output
Going to check whether a number is even or odd Enter the number: 100 The number is even
C Library Functions
Library functions are the inbuilt function in C that are grouped and placed at a common place called the library. Such functions are used to perform some specific operations. For example, printf is a library function used to print on the console. The library functions are created by the designers of compilers. All C standard library functions are defined inside the different header files saved with the extension .h. We need to include these header files in our program to make use of the library functions defined in such header files. For example, To use the library functions such as printf/scanf we need to include stdio.h in our program which is a header file that contains all the library functions regarding standard input/output.
The list of mostly used header files is given in the following table.
| SN | Header file | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | stdio.h | This is a standard input/output header file. It contains all the library functions regarding standard input/output. |
| 2 | conio.h | This is a console input/output header file. |
| 3 | string.h | It contains all string related library functions like gets(), puts(),etc. |
| 4 | stdlib.h | This header file contains all the general library functions like malloc(), calloc(), exit(), etc. |
| 5 | math.h | This header file contains all the math operations related functions like sqrt(), pow(), etc. |
| 6 | time.h | This header file contains all the time-related functions. |
| 7 | ctype.h | This header file contains all character handling functions. |
| 8 | stdarg.h | Variable argument functions are defined in this header file. |
| 9 | signal.h | All the signal handling functions are defined in this header file. |
| 10 | setjmp.h | This file contains all the jump functions. |
| 11 | locale.h | This file contains locale functions. |
| 12 | errno.h | This file contains error handling functions. |
| 13 | assert.h |
This file contains diagnostics functions.
|
- scanf("%d",&n);
- flag = even_odd(n);
- if(flag == 0)
- {
- printf("\nThe number is odd");
- }
- else
- {
- printf("\nThe number is even");
- }
- }
- int even_odd(int n)
- {
- if(n%2 == 0)
- {
- return 1;
- }
- else
- {
- return 0;
- }
- }
- {
- int a,b,result;
- printf("\nGoing to calculate the sum of two numbers:");
- printf("\nEnter two numbers:");
- scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
- result = sum(a,b);
- printf("\nThe sum is : %d",result);
- }
- int sum(int a, int b)
- {
- return a+b;
- }


