C Switch Statement ❮ Edit Details
The switch statement in C is an alternate to if-else-if ladder statement which allows us to execute multiple operations for the different possibles values of a single variable called switch variable. Here, We can define various statements in the multiple cases for the different values of a single variable.
The syntax of switch statement in c language is given below:
- switch(expression){
- case value1:
- //code to be executed;
- break; //optional
- case value2:
- //code to be executed;
- break; //optional
- ......
- default:
- code to be executed if all cases are not matched;
- }
Rules for switch statement in C language
- The switch expression must be of an integer or character type.
- The case value must be an integer or character constant.
- The case value can be used only inside the switch statement.
- The break statement in switch case is not must. It is optional. If there is no break statement found in the case, all the cases will be executed present after the matched case. It is known as fall through the state of C switch statement.
Let's try to understand it by the examples. We are assuming that there are following variables.
- int x,y,z;
- char a,b;
- float f;
| Valid Switch | Invalid Switch | Valid Case | Invalid Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| switch(x) | switch(f) | case 3; | case 2.5; |
| switch(x>y) | switch(x+2.5) | case 'a'; | case x; |
| switch(a+b-2) | case 1+2; | case x+2; | |
| switch(func(x,y)) | case 'x'>'y'; | case 1,2,3; |
Flowchart of switch statement in C
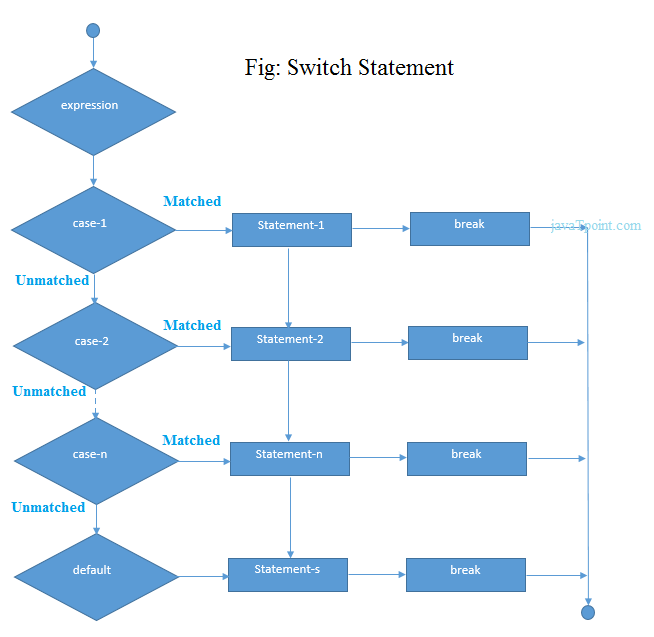
Functioning of switch case statement
First, the integer expression specified in the switch statement is evaluated. This value is then matched one by one with the constant values given in the different cases. If a match is found, then all the statements specified in that case are executed along with the all the cases present after that case including the default statement. No two cases can have similar values. If the matched case contains a break statement, then all the cases present after that will be skipped, and the control comes out of the switch. Otherwise, all the cases following the matched case will be executed.
How does C switch statement work?
Let's go through the step-by-step process of how the switch statement works in C:
Consider the following switch statement:
C Program:
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main() {
- int num = 2;
- switch (num) {
- case 1:
- printf("Value is 1\n");
- break;
- case 2:
- printf("Value is 2\n");
- break;
- case 3:
- printf("Value is 3\n");
- break;
- default:
- printf("Value is not 1, 2, or 3\n");
- break;
- }
- return 0;
- }
Output
Value is 2
Step-by-step Process:
- The switch variable num is evaluated. In this case, num is initialized with the value 2.
- The evaluated num (2) value is compared with the constants specified in each case label inside the switch block.
- The switch statement matches the evaluated value (2) with the constant specified in the second case (case 2). Since there is a match, the program jumps to the code block associated with the matching case (case 2).
- The code block associated with case 2 is executed, which prints "Value is 2" to the console.
- The "break" keyword is present in the code block of case 2. As a result, the program breaks out of the switch statement immediately after executing the code block.
- The program control continues after the switch statement, and any statements following the switch statement are executed. In this case, there are no statements after the switch, so the program terminates.
- The switch statement evaluated the value of the variable num, found a match with case 2, executed the corresponding code block, and then exited the switch block due to the presence of the "break" statement.
Example of a switch statement in C
Let us see a simple example of a C language switch statement.
- #include<stdio.h>
- int main(){
- int number=0;
- printf("enter a number:");
- scanf("%d",&number);
- switch(number){
- case 10:
- printf("number is equals to 10");
- break;
- case 50:
- printf("number is equal to 50");
- break;
- case 100:
- printf("number is equal to 100");
- break;
- default:
- printf("number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100");
- }
- return 0;
- }
Output
enter a number:4 number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100 enter a number:50 number is equal to 50
Switch case example 2
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main()
- {
- int x = 10, y = 5;
- switch(x>y && x+y>0)
- {
- case 1:
- printf("hi");
- break;
- case 0:
- printf("bye");
- break;
- default:
- printf(" Hello bye ");
- }
- }
Output
hi
Break and Default keyword in Switch statement
Let us explain and define the "break" and "default" keywords in the context of the switch statement, along with example code and output.
1. Break Keyword:
The "break" keyword is used within the code block of each case to terminate the switch statement prematurely. When the program encounters a "break" statement inside a case block, it immediately exits the switch statement, preventing the execution of subsequent case blocks. The "break" statement is crucial for avoiding switch statements' "fall-through" behavior.
Example:
Let's take a program to understand the use of the break keyword in C.
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main() {
- int num = 3;
- switch (num) {
- case 1:
- printf("Value is 1\n");
- break; // Exit the switch statement after executing this case block
- case 2:
- printf("Value is 2\n");
- break; // Exit the switch statement after executing this case block
- case 3:
- printf("Value is 3\n");
- break; // Exit the switch statement after executing this case block
- default:
- printf("Value is not 1, 2, or 3\n");
- break; // Exit the switch statement after executing the default case block
- }
- return 0;
- }
Output
Value is 3
Explanation:
In this example, the switch statement evaluates the value of the variable num (which is 3) and matches it with case 3. The code block associated with case 3 is executed, printing "Value is 3" to the console. The "break" statement within case 3 ensures that the program exits the switch statement immediately after executing this case block, preventing the execution of any other cases.
2. Default Keyword:
When none of the case constants match the evaluated expression, it operates as a catch-all case. If no matching case exists and a "default" case exists, the code block associated with the "default" case is run. It is often used to handle circumstances where none of the stated situations apply to the provided input.
Example:
Let's take a program to understand the use of the default keyword in C.
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main() {
- int num = 5;
- switch (num) {
- case 1:
- printf("Value is 1\n");
- break;
- case 2:
- printf("Value is 2\n");
- break;
- case 3:
- printf("Value is 3\n");
- break;
- default:
- printf("Value is not 1, 2, or 3\n");
- break; // Exit the switch statement after executing the default case block
- }
- return 0;
Output
Value is not 1, 2, or 3
Explanation:
In this example, the switch statement examines the value of the variable num (which is 5). Because no case matches the num, the program performs the code block associated with the "default" case. The "break" statement inside the "default" case ensures that the program exits the switch statement after executing the "default" case block.
Both the "break" and "default" keywords play essential roles in controlling the flow of execution within a switch statement. The "break" statement helps prevent the fall-through behavior, while the "default" case provides a way to handle unmatched cases.
C Switch statement is fall-through
In C language, the switch statement is fall through; it means if you don't use a break statement in the switch case, all the cases after the matching case will be executed.
Let's try to understand the fall through state of switch statement by the example given below.
- #include<stdio.h>
- int main(){
- int number=0;
- printf("enter a number:");
- scanf("%d",&number);
- switch(number){
- case 10:
- printf("number is equal to 10\n");
- case 50:
- printf("number is equal to 50\n");
- case 100:
- printf("number is equal to 100\n");
- default:
- printf("number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100");
- }
- return 0;
- }
Output
enter a number:10 number is equal to 10 number is equal to 50 number is equal to 100 number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100
Output
enter a number:50 number is equal to 50 number is equal to 100 number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100
Nested switch case statement
We can use as many switch statement as we want inside a switch statement. Such type of statements is called nested switch case statements. Consider the following example.
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main () {
- int i = 10;
- int j = 20;
- switch(i) {
- case 10:
- printf("the value of i evaluated in outer switch: %d\n",i);
- case 20:
- switch(j) {
- case 20:
- printf("The value of j evaluated in nested switch: %d\n",j);
- }
- }
- printf("Exact value of i is : %d\n", i );
- printf("Exact value of j is : %d\n", j );
- return 0;
- }
Output
the value of i evaluated in outer switch: 10 The value of j evaluated in nested switch: 20 Exact value of i is : 10 Exact value of j is : 20
Advantages of the switch statement:
There are several advantages of the switch statement in C. Some main advantages of the switch statement are as follows:
- Readability and clarity: The switch statement provides a concise and straightforward way to express multiway branching in the code. Dealing with multiple cases can make the code more organized and easier to read than multiple nested if-else statements.
- Efficiency: The switch statement is generally more efficient than a series of if-else statements when dealing with multiple conditions. It works as a direct jump table, which makes it faster and more optimized in terms of execution time.
- Case-based logic: The switch statement naturally fits scenarios where the program needs to make decisions based on specific values of a single variable. It is an intuitive and straightforward way to implement case-based logic.
The switch statement supports using a default case which serves as a catch-all option for values that do not match any provided cases. This default case handles unusual inputs or circumstances that are not expressly stated.
Disadvantages of the switch statement:
There are several disadvantages of the switch statement in C. Some main disadvantages of the switch statement are as follows:
- Limited expressions: The expression used in the switch statement must result in an integral value (char, int, enum) or a compatible data type. It cannot handle more complex or non-constant expressions, limiting its flexibility in some scenarios.
- Inability to compare ranges: Unlike if-else statements, the switch statement cannot handle ranges of values directly. Each case in the switch statement represents a specific constant value, making it challenging to handle a range of values efficiently.
- No support for floating-point numbers: The switch statement only accepts integral types (integers) and values from enums; it does not accept floating-point numbers. It does not handle non-integral data types like floating-point integers, which might be problematic in some circumstances.
- Fall-through behavior: Switch statements have "fall-through" behavior by default which implies that if a case does not include a "break" statement, execution will "fall through" to the following case block. If not managed appropriately, this might result in unwanted behavior.
- Duplicate code: Using a switch statement might result in duplicate code in some circumstances, especially when numerous cases demand the same actions. If not properly managed, this might result in code duplication.
- Nested switches can become complex: When dealing with nested switch statements, the code can become complex and less readable. It may require additional effort to understand and maintain such nested structures.
4vkynfSx


