for loop in C ❮ Edit Details
The for loop in C language is used to iterate the statements or a part of the program several times. It is frequently used to traverse the data structures like the array and linked list.
Syntax of for loop in C
The syntax of for loop in c language is given below:
- for(Expression 1; Expression 2; Expression 3){
- //code to be executed
- }
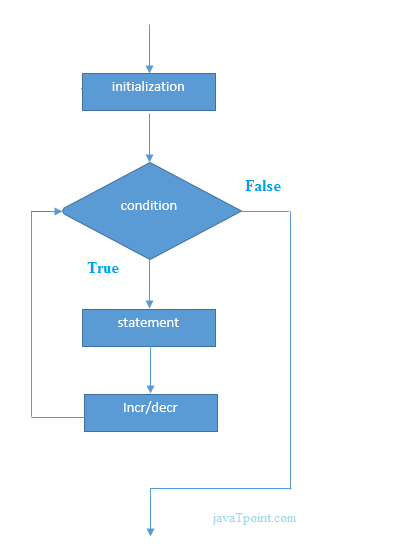
Flowchart of for loop in C
C for loop Examples
Let's see the simple program of for loop that prints table of 1.
- #include<stdio.h>
- int main(){
- int i=0;
- for(i=1;i<=10;i++){
- printf("%d \n",i);
- }
- return 0;
- }
Output
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
C Program: Print table for the given number using C for loop
- #include<stdio.h>
- int main(){
- int i=1,number=0;
- printf("Enter a number: ");
- scanf("%d",&number);
- for(i=1;i<=10;i++){
- printf("%d \n",(number*i));
- }
- return 0;
- }
Output
Enter a number: 2 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
Enter a number: 1000 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 8000 9000 10000
Properties of Expression 1
- The expression represents the initialization of the loop variable.
- We can initialize more than one variable in Expression 1.
- Expression 1 is optional.
- In C, we can not declare the variables in Expression 1. However, It can be an exception in some compilers.
Example 1
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main()
- {
- int a,b,c;
- for(a=0,b=12,c=23;a<2;a++)
- {
- printf("%d ",a+b+c);
- }
- }
Output
35 36
Example 2
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main()
- {
- int i=1;
- for(;i<5;i++)
- {
- printf("%d ",i);
- }
- }
Output
1 2 3 4
Properties of Expression 2
- Expression 2 is a conditional expression. It checks for a specific condition to be satisfied. If it is not, the loop is terminated.
- Expression 2 can have more than one condition. However, the loop will iterate until the last condition becomes false. Other conditions will be treated as statements.
- Expression 2 is optional.
- Expression 2 can perform the task of expression 1 and expression 3. That is, we can initialize the variable as well as update the loop variable in expression 2 itself.
- We can pass zero or non-zero value in expression 2. However, in C, any non-zero value is true, and zero is false by default.
Example 1
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main()
- {
- int i;
- for(i=0;i<=4;i++)
- {
- printf("%d ",i);
- }
- }
output
0 1 2 3 4
Example 2
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main()
- {
- int i,j,k;
- for(i=0,j=0,k=0;i<4,k<8,j<10;i++)
- {
- printf("%d %d %d\n",i,j,k);
- j+=2;
- k+=3;
- }
- }
Output
0 0 0 1 2 3 2 4 6 3 6 9 4 8 12
Example 3
- #include <stdio.h>
- int main()
- {
- int i;
- for(i=0;;i++)
- {
- printf("%d",i);
- }
- }
Output
infinite loop
Properties of Expression 3
- Expression 3 is used to update the loop variable.
- We can update more than one variable at the same time.
- Expression 3 is optional.
Example 1
- #include<stdio.h>
- void main ()
- {
- int i=0,j=2;
- for(i = 0;i<5;i++,j=j+2)
- {
- printf("%d %d\n",i,j);
- }
- }
Output
0 2 1 4 2 6 3 8 4 10
Loop body
The braces {} are used to define the scope of the loop. However, if the loop contains only one statement, then we don't need to use braces. A loop without a body is possible. The braces work as a block separator, i.e., the value variable declared inside for loop is valid only for that block and not outside. Consider the following example.
- #include<stdio.h>
- void main ()
- {
- int i;
- for(i=0;i<10;i++)
- {
- int i = 20;
- printf("%d ",i);
- }
- }
Output
20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20
Infinitive for loop in C
To make a for loop infinite, we need not give any expression in the syntax. Instead of that, we need to provide two semicolons to validate the syntax of the for loop. This will work as an infinite for loop.
- #include<stdio.h>
- void main ()
- {
- for(;;)
- {
- printf("welcome to javatpoint");
- }
- }
If you run this program, you will see above statement infinite times.


